1. Introduction
GR8 CRM is a set of Grails Web Application Framework plugins that makes it easy to develop web applications with CRM functionality.
You can find more information about GR8 CRM on the main documentation site http://gr8crm.github.io.
1.1. Customer Relationship Management
Customer relationship management (CRM) is a system for managing a company’s interactions with current and future customers. It involves using technology to organize, automate and synchronize sales, marketing, customer service, and technical support. Wikipedia
The GR8 CRM "Ecosystem" currently contains over 40 Grails plugins. For a complete list of plugins see http://gr8crm.github.io.
Each GR8 CRM plugin defines a Bounded Context that focus on one specific domain, for example contact, project or document.
2. Blog Services Plugin
This plugin provide storage and services for managing blogs in GR8 CRM applications. A blog post is just a HTML document with some extra properties. You could probably use the crm-content plugin to write blog posts and publish on a web page but the crm-blog plugin together with crm-blog-ui makes blog authoring much easier.
The crm-blog plugin does not duplicate code or features in crm-content plugin. Instead it depends on crm-content and delegate much of the storage and rendering to crm-content.
Note that this plugin does not contain any user interface components. This plugin contains domain classes and services only. The plugin crm-blog-ui provides a Twitter Bootstrap based user interface for blog authors.
2.1. Rendering blog posts
To render blog posts in a GSP page you can use the crm:blogPosts tag. It iterates over all published blog posts and render it’s content on the page. The following example show that:
<crm:blogPosts var="post" query="${[status: 'published']}" params="${[max: 20, sort: 'date', order: 'desc']}">
<div class="crm-blog-post" id="${post.name}">
<g:link action="show" id="${post.name}"><h2>${post.title.encodeAsHTML()}</h2></g:link>
<p class="lead">${post.description?.encodeAsHTML()}</p>
<div>
<span class="muted" style="font-size: 12px;">
Published <g:formatDate format="d MMM yyyy" date="${post.date}"/>
</span>
</div>
<div class="crm-blog-body">
<crm:render template="${post.template}" parser="${post.parser}" model="${post}"/>
</div>
<p class="crm-blog-tags">
<span class="muted">Tags:</span>
<g:each in="${post.tags()}" var="tag">
<span class="label label-info">${tag.encodeAsHTML()}</span>
</g:each>
</p>
<hr/>
</div>
</crm:blogPosts>The example above render something like this:
The crm:blogPosts tag is included in the crm-blog plugin so you could create a Grails application that serves a public web site and include the crm-blog plugin to render blog posts. Then you could create another Grails application and include the crm-blog-ui plugin to get all the blog editing features that your blog authors use to create content. Or you can include both plugins in the same application if it’s a small project with limited requirements.
3. Domain model
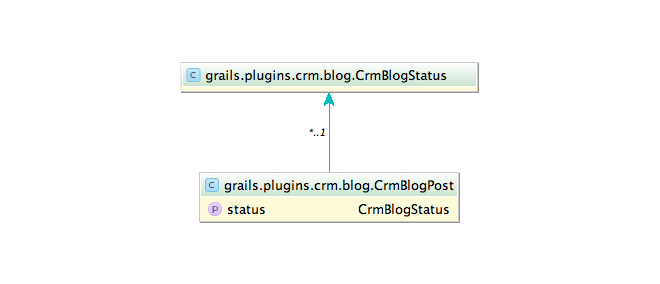
4. CrmBlogService
The CrmBlogService provide methods for creation and management of blog posts.
4.1. Create a new blog post
CrmBlogPost createBlogPost(Map params, boolean save = false)
def published = crmBlogService.createBlogStatus(name: "Published", true)
def post = crmBlogService.createBlogPost(status: published, name: "test",
title: "Test post", description: "This is my first test", date: new Date(), true)
To create a new blog post you call createBlogPost with a Map of values. The save parameter controls if the blog post should be persisted immediately or just initialized with values. This does only create the metadata for the blog post. The actual HTML content is created separately.
crmContentService.createResource('<h1>TEST</h1><p>Hello World</p>', 'content.html', post, [contentType: 'text/html'])
You see that we leverage crmContentService from the crm-content plugin. That plugin is automatically included by the crm-blog plugin with a compile-time dependency. So all features in crm-content are available when you use the crm-blog plugin.
4.2. Retrieve a blog post
CrmBlogPost getBlogPost(Long id)
To retrieve a blog post by it’s primary key you can use getBlogPost().
4.3. Search for blog posts
def list(Map query, Map params)
Query blog posts with the list() method.
The following key kan be used in the query map. Pagination and sorting keys goes into the params map.
-
title (wildcard)
-
username
-
status (wildcard)
-
fromDate (date)
-
toDate (date)
4.4. Archive an old blog post
boolean archiveBlogPost(CrmBlogPost post)
This method sets the status to archived. This is a special CrmBlogStatus with the param property set to archived. You can change the parameter to something else with the configuration option crm.blog.status.archived.
4.5. Delete a blog post
String deleteBlogPost(CrmBlogPost crmBlogPost)
Deletes a blog post. The blog post toString() value is returned after successful deletion.
5. Changes
- 2.4.1
-
Plugin upgraded to Grails 2.4.5
- 2.4.0
-
First public release
6. License
This plugin is licensed with Apache License version 2.0
7. Source Code
The source code for this plugin is available at https://github.com/technipelago/grails-crm-blog
8. Contributing
Please report issues or suggestions.
Want to improve the plugin: Fork the repository and send a pull request.