1. Introduction
GR8 CRM is a set of Grails Web Application Framework plugins that makes it easy to develop web applications with CRM functionality.
You can find more information about GR8 CRM on the main documentation site http://gr8crm.github.io.
1.1. Customer Relationship Management
Customer relationship management (CRM) is a system for managing a company’s interactions with current and future customers. It involves using technology to organize, automate and synchronize sales, marketing, customer service, and technical support. Wikipedia
The GR8 CRM "Ecosystem" currently contains over 40 Grails plugins. For a complete list of plugins see http://gr8crm.github.io.
Each GR8 CRM plugin defines a Bounded Context that focus on one specific domain, for example contact, project or document.
2. Contact Management Plugin
The crm-contact plugin is the most frequently used plugin in GR8 CRM applications. CRM is about managing customers and customer interactions. This plugin provides storage and services for managing companies, people and relationships between them. You can use it as a simple address book or as the base of a complex customer relationship management system. The plugin is generic but flexible, it has proven support for many different use-cases.
Note that this plugin does not contain any user interface components. This plugin contains domain classes and services only. The plugin crm-contact-ui provides a Twitter Bootstrap based user interface for managing contacts and relations. crm-contact-ui depends on crm-contact so you only need to include crm-contact-ui in your BuildConfig.groovy if you want end-user contact management features.
3. Domain Model
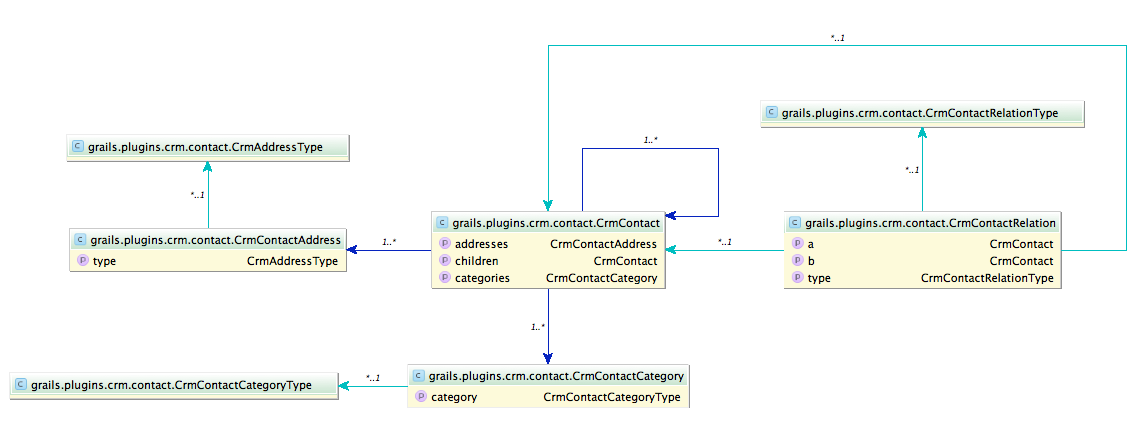
3.1. CrmContact
This is the main domain class that store contacts. It stored companies and individuals in the same domain class. A person uses firstName and lastName properties but companies uses only the name property.
| Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
firstName |
String |
Given name(s) for person, null for company. |
lastName |
String |
Family name for person, null for company. |
name |
String |
firstName + lastName (set in beforeValidate) for individuals and complete name for company |
number |
String |
Customer number |
number2 |
String |
Extra customer number |
ssn |
String |
Social Security Number (personnr/orgnr in Sweden) |
duns |
String |
D&B D-U-N-S™ identification number. |
description |
String |
Description or short notes about the contact |
title |
String |
Business title |
String |
Main email address |
|
telephone |
String |
Main telephone number |
mobile |
String |
Cellular phone number |
fax |
String |
Fax number |
url |
String |
The contact’s web site |
3.2. CrmContactRelation
This domain class links two contacts together. An example would be to link an employee to it’s employer. The type of relation is specified by the type property that references a CrmContactRelationType.
4. CrmContactService
CrmContact getContact(Long id)
Find a contact based on primary key.
CrmContact findByNumber(String number)
Find a contact based on customer number.
CrmContact findByName(String name)
Find a contact based on name.
PagedResultList<CrmContact> list(Map query, Map params)
List contacts using query by example parameters.
CrmContact createCompany(Map<String, Object> params, boolean save = false)
Create a new company.
CrmContact createPerson(Map<String, Object> params, boolean save = false)
Create a new person.
String deleteContact(CrmContact crmContact)
Delete an existing contact.
5. Code Samples
5.1. Create a company
To create a new company and store it in the database you use crmContactService.createCompany(Map, boolean)
def technipelago = crmContactService.createCompany(name: "Technipelago AB", email: "info@technipelago.se",
url: "www.technipelago.se", address: [postalCode: "13973", city: "Djurhamn", country: "Sweden"], true)The last parameter is true, this means that the company should be persisted (saved) to the database. If the last parameter is false or omitted all properties will be set from the specified Map but the company will not be persisted. You can later call save() on the instance if you need to perform extra steps before persisting.
5.2. Create a person
To create a new person and store it in the database you use crmContactService.createPerson(Map, boolean)
def goran = crmContactService.createPerson(firstName: "Göran", lastName: "Ehrsson",
email: "goran@technipelago.se", title: "Developer", true)The last parameter is true, this means that the person should be persisted (saved) to the database. If the last parameter is false or omitted all properties will be set from the specified Map but the person will not be persisted. You can later call save() on the instance if you need to perform extra steps before persisting.
5.3. Relations
Relations are used to connect contacts together. To connect an employee with it’s employer you create a CrmContactRelation between them. The domain class CrmContactRelation has a property called primary that specifies what relation is the primary relation for that contact. A contact can have many relations but only one primary relation. A good example is the employee←→employer relation, were the relation from the person to it’s employer (company) has the primary property set to true. This affects things like address management and display of contact information.
def relation = crmContactService.addRelation(goran, technipelago, 'employer', true)5.4. Search Contacts
To query the database for contact you can use crmContactService.list(Map, Map). This first parameter accepts a map of query values. The second parameter is a map with pagination parameters (offset, max, sort, order).
def result
result = crmContactService.list([name: "Göran"], [:]) (1)
println result
[Göran Ehrsson]
result = crmContactService.list([name: "Tech"], [:]) (2)
println result
[Technipelago AB]
result = crmContactService.list([person: true, related: "Tech"], [:]) (3)
println result
[Göran Ehrsson]| 1 | Find contacts who’s name begins with "Göran" |
| 2 | Find contacts who’s name begins with "Tech" |
| 3 | Find contacts of type person that have a relation to a contact who’s name begins with "Tech" |
6. Changes
- 2.4.4
-
Depends on crm-core version 2.4.4 that include increased column lengths for some address properties
- 2.4.3
-
Increase length of name field from 80 to 128 characters → db migration!
- 2.4.2
-
Added
CrmContactService#getRelatedContacts(). Improved sequence number configuration. - 2.4.1
-
Relevant classes now implements interfaces CrmContactInformation and CrmAddressInformation (crm-core 2.4.2)
- 2.4.0
-
First version compatible with Grails 2.4.4.
- 2.0.2
-
Changes due to CrmContactInformation interface changes in plugin crm-core version 2.0.1.
New method Long CrmContact#getCompanyId(). - 2.0.1
-
Fixed bug in CrmContactService#list(Map, Map) where query on related returned ID:s for the related contact, it should return self side only.
Added support for passing key related to CrmContactService#createPerson(Map, boolean) to automatically create a relation to another contact. - 2.0.0
-
First public release
7. License
This plugin is licensed with Apache License version 2.0
8. Source Code
The source code for this plugin is available at https://github.com/goeh/grails-crm-contact
9. Contributing
Please report issues or suggestions.
Want to improve the plugin: Fork the repository and send a pull request.